Answering Your Questions About Psoriasis
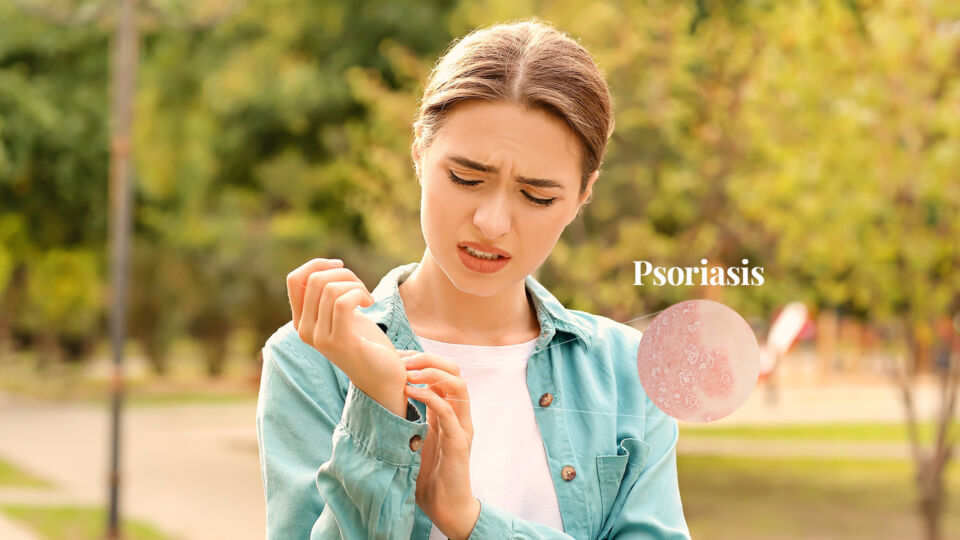

Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that presents with red scaly patches on the skin. It is a non-infectious disease that affects all races regardless of age. The commonly affected areas are the elbows, knees, and scalp. Nail changes, like pits in the nail plate and separation of the nail from the nail bed, are often seen in nearly half of the affected patients.
Joints may also be affected, resulting in joint pain and swelling.
According to a 2016 report1 by World Health Organisation, psoriasis affects approximately 100 million people worldwide. In Singapore, it is estimated that at least 40,000 persons are affected with psoriasis2.
What Are the Common Symptoms of Psoriasis?
There are signs and symptoms of psoriasis to look out for to determine if you are affected by it. They are as follows: most common ones to look out for are firstly,
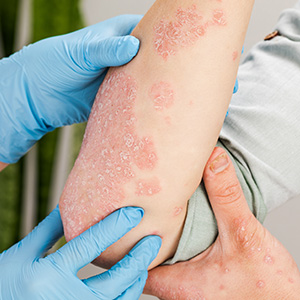
Patchy Rash on Skin
This is the most common symptom of psoriasis. The size and intensity of the rash varies for every individual. The rashes are mostly scaly and red.
Small Scaling Spots
Also known as guttate psoriasis, this symptom is commonly found in children and young adults. It is usually triggered by a bacterial infection.
Cyclic Rashes
Flaring of skin rashes that may last for weeks or months.
Triggers for Psoriasis
As psoriasis is not contagious, there are other triggers that might bring about the disease. These are either caused by genetics, environmental factor, or a combination of both.
Some of the common triggers are:
- Stress: physical, emotional, and mental
- Injury to the skin caused by scratching, peeling, rubbing, or even sunburn
- Infections of the chest, throat, and urinary tract
- Oral medication such as steroids, beta-blockers, anti-malarial, etc
- Obesity, alcohol abuse, and smoking
What Are the Types of Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is not limited to visible skin rash. There are different types of psoriasis and they are as follows:
Plaque Psoriasis
- Most common type
- Causes dry itchy skin patches
Nail Psoriasis
- Affects fingernails and toenails
- Cause abnormal nail growth and discoloration
Guttate Psoriasis
- Primarily affects young adults and children
- Triggered by bacterial infection
Inverse Psoriasis
- Affects skin folds of groin, buttocks, and breast
- Cause smooth patch of inflamed skin
Pustular Psoriasis
- Rare type
- Pus filled blisters
Erythrodermic Psoriasis
- Least common type
- Can cover entire body with a peeling rash
- Short-term or chronic
Can Psoriasis Be Treated?
There are different treatment plans available for individuals. The aim for psoriasis treatment is to slow down the speed of the growth of skin cells, as well as to remove scales on the skin surface.
Some of the available treatments include but are not limited to:
- Topical creams or ointments
- Phototherapy with the use of light
- Usage of oral or injected medications such as biologics
Treatment methods may differ from one individual to another, depending on the severity of one’s condition.
If you suspect that you may have psoriasis, consult a doctor as soon as possible because a delay in treatment may cause the condition to worsen.
2Psoriasis Association of Singapore.

 Our
Our 

